Thawing meat might seem as simple as waiting for it to warm up, but it’s a culinary dance that requires finesse and timing. Imagine planning a delicious dinner only to realize your chicken is still frozen solid. Panic sets in, and suddenly, takeout starts looking like a five-star meal. But fear not! Understanding how long meat takes to thaw can save the day and your dinner plans.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Thawing
Thawing meat involves transitioning it from a frozen state to a temperature suitable for cooking. Various factors influence this process, including the type of meat, its weight, and the method used for thawing. Understanding these variables helps ensure safe and effective thawing.
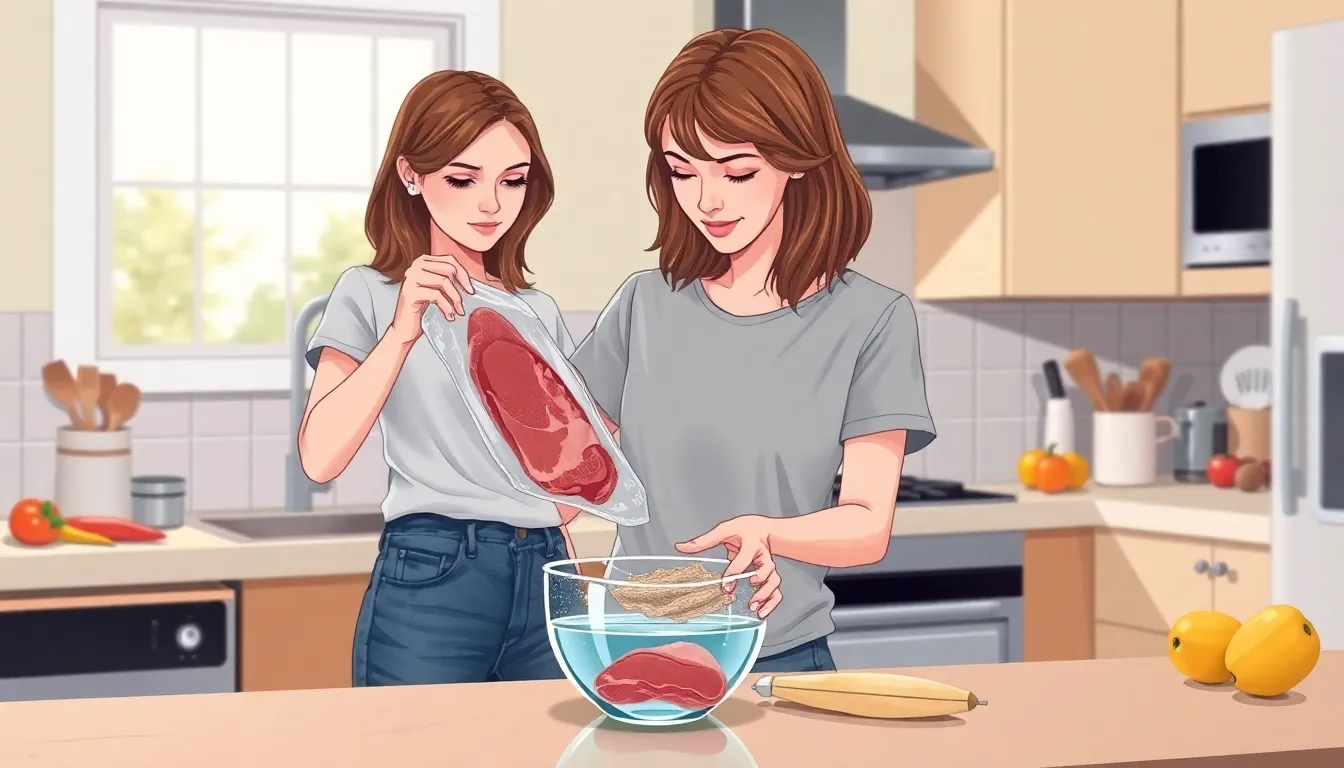
Refrigerator thawing remains the safest method. For every five pounds of meat, plan for 24 hours in the fridge. Thicker cuts, like a whole turkey, may require several days; a 20-pound turkey needs about four to five days for optimal thawing.
Another option is cold water thawing, which requires more attention but is faster. Submerge the meat in cold water, changing it every 30 minutes. A one-pound package of chicken breasts thaws in about an hour, while a five-pound roast may take approximately three hours.
Microwave thawing provides speed but demands caution. When using this method, cook the meat immediately after thawing since some areas may become warm enough to begin cooking. A pound of ground beef thaws in about eight minutes, while larger cuts may take a bit longer.
Improper thawing increases the risk of bacterial growth. Keeping meat at temperatures above 40°F for more than two hours raises potential health concerns. Opt for proper thawing methods to maintain food safety and quality.
Choosing the right thawing technique aligns with meal preparation timelines and safety. Prioritizing these methods can alleviate stress during busy cooking times, allowing for enjoyable meal experiences.
Factors Affecting Thawing Time
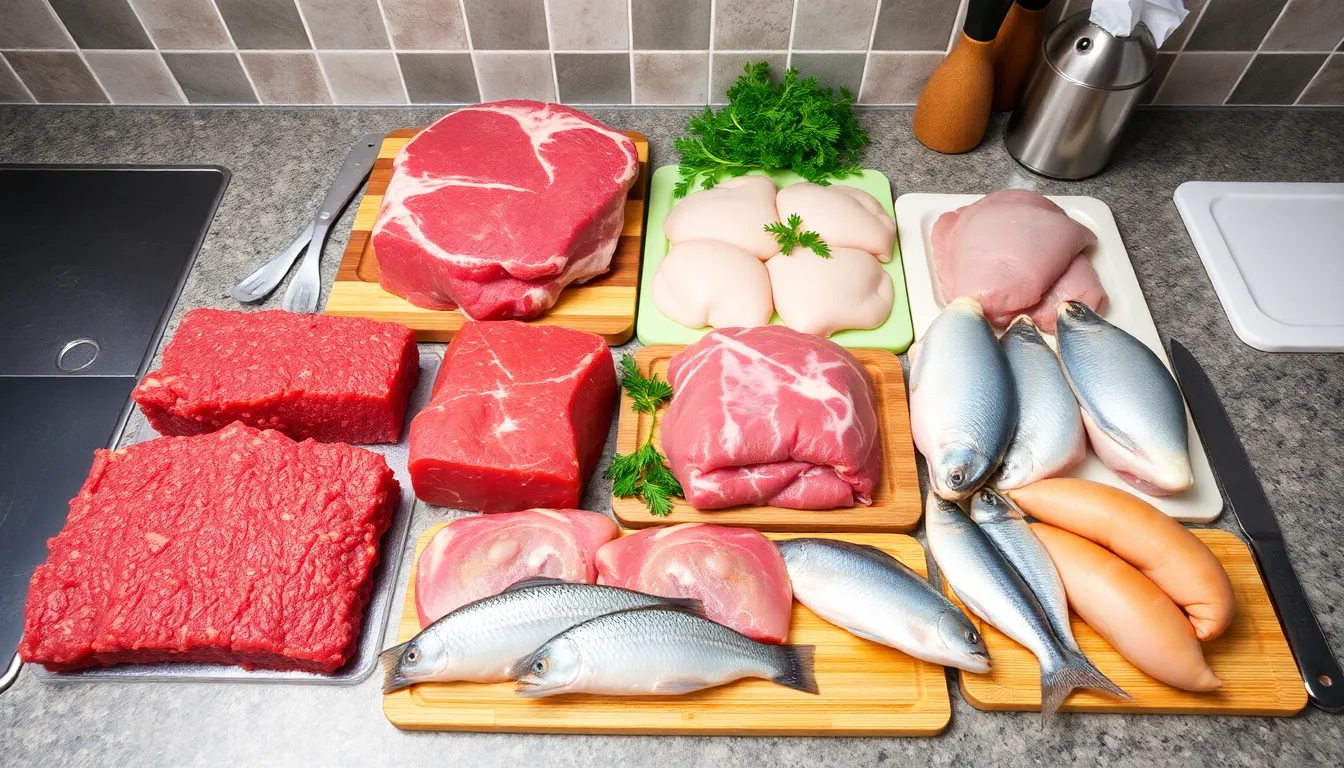

Several elements impact how long meat takes to thaw. Understanding these factors can enhance meal preparation and ensure food safety.
Type of Meat
Different types of meat thaw at varying rates. Ground meats, such as beef or turkey, typically thaw quicker than larger cuts like roasts or whole chickens. Poultry tends to thaw faster compared to beef or pork due to its lower density. Fish also thaws rapidly, often in less than an hour using cold water methods. Knowing the type of meat allows for better planning in cooking times and techniques, helping to avoid delays in meal preparations.
Thickness of Cuts
The thickness of meat cuts significantly influences thawing duration. Thicker cuts require more time, as the center remains frozen longer. A steak that is 1 inch thick thaws faster than a 2-inch thick roast. On average, thin cuts of meat may thaw in under an hour using cold water, while thicker cuts might take several hours to fully thaw. Thawing methods may need adjustment based on cut thickness to ensure safe cooking temperatures are reached efficiently.
Recommended Thawing Methods
Proper thawing methods ensure food safety and enhance the cooking experience. Three commonly used techniques are refrigerator thawing, cold water thawing, and microwave thawing.
Refrigerator Thawing
Refrigerator thawing is the safest method for defrosting meat. Typically, it takes 24 hours for every five pounds of meat, so planning ahead is crucial. Larger cuts like whole turkeys might require several days. While this method is slow, it keeps meat at a safe temperature, reducing the risk of bacterial growth. This technique allows for flexible meal planning since meat can remain in the refrigerator for an additional day or two before cooking.
Cold Water Thawing
Cold water thawing speeds up the process compared to refrigerator thawing. To use this method, place sealed meat in a bowl of cold water, changing the water every 30 minutes. Most small cuts can thaw in about one hour, while larger items may take up to two to three hours. This method necessitates cooking the meat immediately after thawing to prevent any health risks. Careful attention during the process ensures the meat’s safety and quality.
Microwave Thawing
Microwave thawing provides the quickest solution for defrosting meat. Using the defrost setting, it takes minutes to thaw smaller cuts, while larger pieces may require multiple cycles. Although effective, this method causes some parts of the meat to begin cooking, so immediate cooking follows thawing. Thoroughly checking the meat ensures all areas of it have reached a consistent temperature. With this method, users must handle meat carefully to avoid uneven thawing and preserve quality.
Safety Considerations
Thawing meat safely is crucial to prevent foodborne illness. Bacteria can multiply rapidly when meat is held at temperatures between 40°F and 140°F for more than two hours. Priority should be given to methods that minimize these risks, such as refrigerator thawing. It keeps meat at a consistent, safe temperature, allowing the meat to remain below the danger zone throughout the thawing process.
Cold water thawing should be done carefully. Submerging meat in cold water speeds up thawing but requires constant attention. Changing the water every 30 minutes ensures the meat maintains a safe temperature and minimizes bacterial growth. It’s essential to cook meat immediately after cold water thawing.
Microwave thawing is effective for quick meals, yet it comes with challenges. Uneven thawing often happens, leading to partially cooked areas that bacteria can thrive in. Cooking the meat right after microwave thawing eliminates safety concerns.
Cross-contamination is another critical factor. Always keep thawed meat separate from other foods, especially those eaten raw. Using separate utensils and cutting boards helps prevent the spread of harmful bacteria.
Monitoring meat temperature can further enhance safety. Using a food thermometer ensures meat reaches a safe internal temperature: for poultry, it should hit 165°F, while beef, pork, and lamb benefit from reaching at least 145°F.
These guidelines on meat thawing underscore the importance of safety. Proper thawing techniques lead to healthier meals and a more enjoyable cooking experience. Awareness and planning can significantly reduce safety risks in food preparation.
Conclusion
Thawing meat properly is essential for both safety and quality. By understanding the different methods and their respective times, anyone can avoid the stress of last-minute meal planning. Prioritizing refrigerator thawing ensures safety and flexibility while cold water and microwave methods offer quicker alternatives when time is tight.
Being mindful of the type of meat and its thickness can further streamline the thawing process. With these insights in hand, preparing delicious and safe meals becomes a manageable task. Following these guidelines leads to better cooking experiences and healthier meals for everyone.